Google Analytics 4 Review & Beginner’s Implementation Guide
Users have trusted Universal Analytics throughout many years to track user behavior and optimize their campaign strategies. Suddenly, Google announces a major shift: The analytics tool Universal Analytics faces retirement through implementation of Google Analytics 4 (GA4). Your business faces unknown changes from this new development.
A significant number of marketers alongside business owners encountered this specific challenge. GA4 represents a whole new system over Universal Analytics since it combines advanced analytic capabilities with cross-platform measurement and privacy-protecting features. This text will analyze the fresh elements in GA4 together with a starting approach.
Table of Contents
The Key Differences Between GA4 and UA
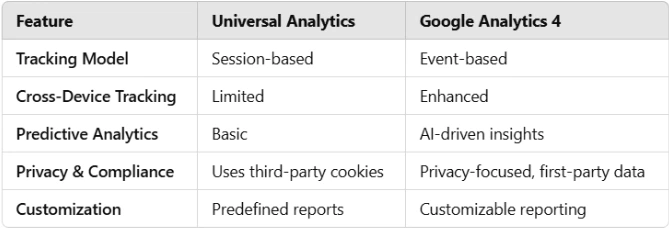
UA was of huge help to businesses for a long time, however, the digital landscape has shifted. GA4 is meant for the future with its focus on AI analytics as well as user engagement. Here is a comparison between them:
Firms now have to transition much faster because GA4 has enhanced privacy protections which requires more detailed reporting.
Narrative: How Riya Increased Conversions with GA4
A vacation website was being run by Riya, a freelance digital marketing strategist in Kochi. She saw a decrease in conversions, but she was unable to identify the cause with Universal Analytics. Following her switch to GA4, she:
- found that although people were interacting with blog posts, they were not clicking on links to make reservations.
- To track “Book Now” button clicks, set up event-based tracking.
- Using GA4’s AI-powered insights, it was discovered that a slow-loading payment page was the reason why users on mobile devices abandoned reservations.
In just three months, Riya raised conversions by 30% by making the mobile experience better!
Google Analytics 4: What’s New?
GA4 offers a number of strong capabilities to assist companies in making more informed decisions based on data:
1. Tracking by Events
Event-based tracking takes the role of session-based tracking and conventional pageviews. This implies that all user interactions, including clicks, video plays, and downloads, are recorded as events.
- For instance, a fitness website can monitor the number of users who finish a training video, offering insightful data on user engagement.
2. Predictive Analytics Driven by AI
GA4 helps organizations optimize advertising by using machine learning to predict user behavior.
- For instance, an online retailer can determine which customers are most likely to buy something within the next seven days and offer them exclusive deals.
3. Cross-Device & Cross-Platform Monitoring
GA4 provides a unified view of customer journeys by combining data from mobile apps and websites.
- For instance, a restaurant app can monitor customers who use their mobile device to peruse the menu before placing a desktop order.
4. Data Collection with a Privacy Focus
By emphasizing first-party data and giving users discretion over data sharing, GA4 conforms with GDPR and CCPA rules in light of the growing concerns about data privacy.
For instance, a financial business can monitor user activity while maintaining adherence to privacy regulations.
5. Customized Insights & Reports
More reporting flexibility is provided by GA4, enabling companies to customize insights to meet their unique requirements.
- For instance, a digital firm can design unique dashboards that solely provide conversion stats for a number of clients.
How to Begin Using GA4
Step 1: Configure the GA4 Property.
GA4 can be set up in conjunction with Universal Analytics if you already have it:
- Navigate to Admin → Create Property in Google Analytics.
- Choose GA4 and configure data streams for tracking websites and applications.
Step 2: Turn on Enhanced Measurement.
Scrolls, file downloads, and outbound clicks are among the interactions that GA4 automatically records. Under Admin → Data Streams → Web, turn on these functionalities.
Step 3: Identify Important Occurrences and Conversions.
Define the most pertinent user behaviors because GA4 tracks events rather than goals:
- Purchase completion
- Put in the cart
- Signing up for a newsletter
To set up custom event tracking, use Google Tag Manager.
Step 4: Connect BigQuery and Google Ads.
GA4 should be integrated with Google Ads to enhance ad performance. For more in-depth insights, companies seeking sophisticated data analysis can transfer raw GA4 data to BigQuery.
Step 5: Personalize Dashboards and Reports
GA4 provides powerful, customizable reporting tools:
- To examine user behavior, utilize Exploration Reports.
- Build Funnels & Path Analysis to track customer journeys.
Challenges & How to Overcome Them
1. Learning Curve
Many marketers find GA4 complex at first. Solution? Follow Google’s instructions and explore with sample accounts.
2. Limitations of Historical Data
Data from Universal Analytics is not imported into GA4. The answer? Continue to run UA in parallel until enough GA4 data is gathered.
3. Customization Efforts
GA4 requires companies to manually define key metrics, in contrast to UA. The answer? Invest time in setting up reports to meet company objectives.
Why Businesses Must Adopt GA4 Now
- Universal Analytics Will Stop Processing Data: As of July 2023, UA has been phased out.
- Better Insights for Smarter Decisions: AI-powered analytics enable predictive marketing.
- Future-Proof Data Strategy: GA4 is designed to work in a privacy-first world.
Conclusion: GA4 is the future.
Google Analytics 4 is more than simply an update; it’s a completely new way to monitor and examine user data. For businesses and marketers, switching to GA4 today guarantees they stay ahead of the curve. Whether you are a freelance digital marketing strategist or brand owner, learning GA4 will open up new avenues for growth and marketing strategy optimization.
Author Info
Nima Mary James, A Freelance Digital Marketing Strategist in Kochi.
Learner of CDA Online Digital Marketing Course in India.